Guava (Psidium guajava) is a tropical fruit that is oval and originated from Central America and Mexico. It is the fourth most significant fruit after mango, banana, and citrus. Later, Guavaguava is harvested across Asia and predominantly on the Indian subcontinent. There are around 30 varieties of Guava in India. However, white Guavaguava and pink Guavaguava are India’s most commonly cultivated Guava varieties. The Guavaguava is a tiny five-petal, white flower with numerous stamens before becoming a fruit. The appearance of Guavaguava is greenish-yellow on the outside with white or pink flesh inside, and the meat is loaded with seeds.
Varieties of Guava in India
There are wide varieties of Guava in India. However, White Guava and Pink Guavaguava are fruit pulp manufacturers’ most preferred Guava varieties in India. The Indian guava varieties are named on the skin and pulp colour. Some types of guava in India are called according to the place of origin and shape. Allahabad Safeda and Sardar varieties dominate the Indian market because of their yielding capacity, excellent quality, and acceptance worldwide. The popular types of Guavaguava in India are Allahabad Safeda, Sardar (Lucknow 49), Pant Prabhat, Lalit, Dhareedar, Chittidar, Harijan, Arka Mridula, and Khaja (Bengal Safeda). Hybrid varieties like Safed jam, Kohir Safeda, and Arka Amulya were also developed.
The Lucknow variety of Guavaguava is cultivated in Nuzvid, Vijayawada, and Andhra Pradesh and is used for pulping. Safeda variety is produced in Odugathur, Bangalore, and Tadipatri and is used as a pulping and table variety. The Allahabad variety is grown in Madurai, Theni, and Dindigul and used as a table variety. Indian guava varieties are used as a table variety and for manufacturing fruit pulps. White Guavaguava and pink guava varieties are the most popular in manufacturing pulp, puree, and concentrate.
Pink Guavaguava is one of the popular varieties of Guavaguava in India. The desi Karnataka variety of pink Guavaguava is used in the pulping industry. Taiwan, Arka Kiran varieties are grown in the region of Tadipatri and Vijayawada and are used as table varieties. Pink guava varieties are used mainly in food processing industries because of their natural sweetness and higher pulp content. Indian guava varieties with more Brix value are preferred by pulp and beverage producers to have a better taste and sweetness in drinks.
Guava production In India and the rest of the world
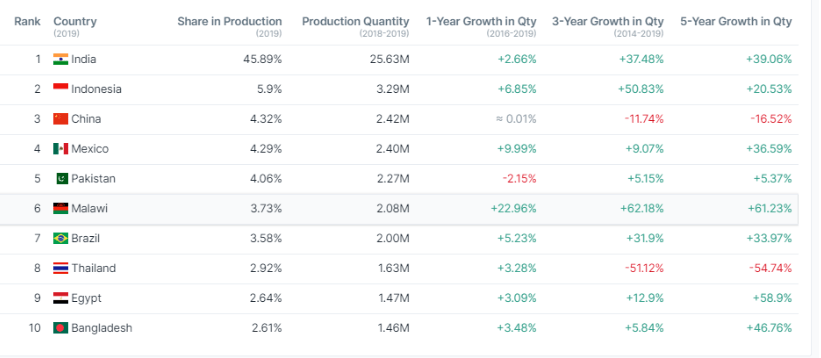
India is the world’s largest producer of Guavaguava, which harvests 25M metric tons, contributing to 45% of the world’s guava production. The second and third largest producers are Indonesia and China, which donate 7% and 5% of the output. Per the reports till 2019, guava production in India witnessed a 5% annual growth. Thailand becomes the top exporter with a 15% yearly growth, and China becomes the biggest importer with a 15% increase annually.
Guava production worldwide continues to increase in Asian countries due to favourable climatic conditions. As per the reports of world guava production in 2019, Indonesia shares a 5.9% share of output with a production quantity of 3.29M metric tons. China and Mexico share a 4% share in production and expect a rise in production in upcoming years.
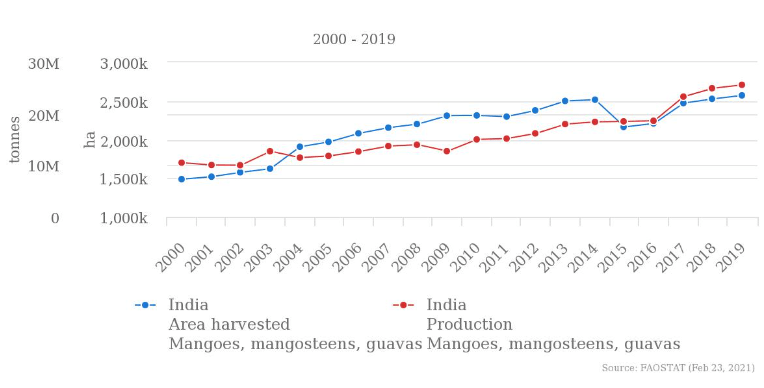
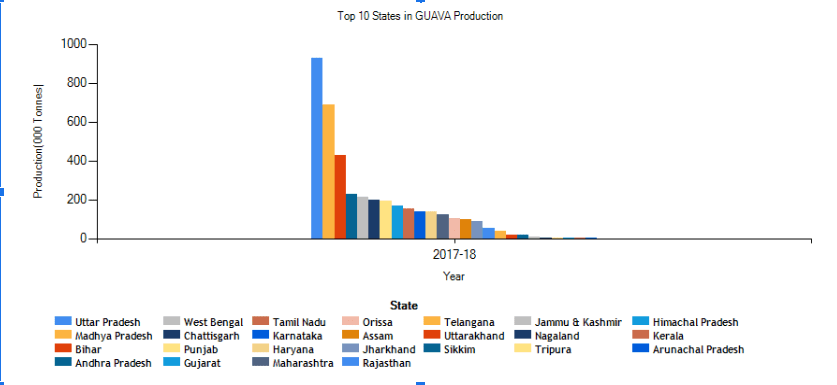
Although Guavaguava can be grown throughout India due to favourable climatic conditions, Uttar Pradesh is the major contributor in production, followed by Punjab, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Tamilnadu. Where farming has been gaining popularity recently, harvesting in India has increased by 64%, and guava production in India to 55% over the past four decades. Guava is grown in tropical and subtropical regions and tolerates high temperatures, which makes India a favourable place to harvest guavas. In Tamilnadu, guavas are predominantly cultivated in Madurai, Salem, and Dindigul. The below chart shows the Guavaguava producing states in India. Uttar Pradesh is India’s largest producer of guava, producing 928.44 tonnes with a market share of 22.93%. Madhya Pradesh and Bihar are India’s second and third-largest guava-producing states, with 16% and 10% market shares, respectively.
Harvesting Seasons of Guava
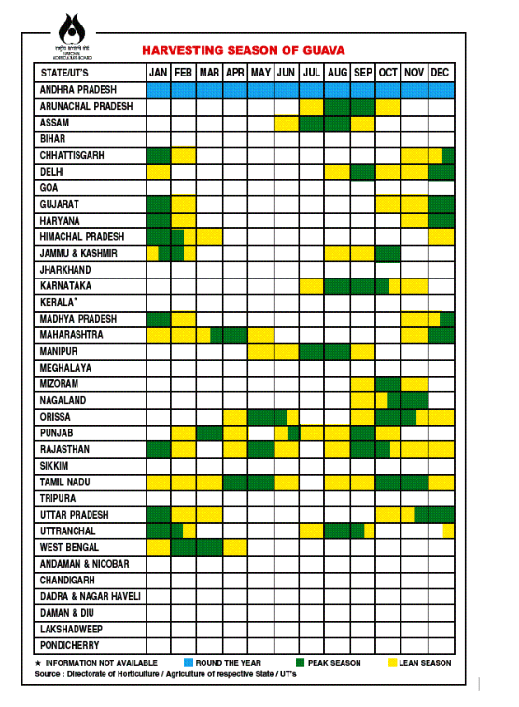
The Guava plants start bearing fruits at 2-3 years but attain a total bearing capacity at 8-10 years. A plant’s yield depends on its cropping pattern, age, and cultural practices—a 10-year-old plant yields between 10 and 100 kgs of guava fruits per year. Guavas are cultivated throughout the year in Andhra Pradesh, and the peak guava growing season in north India is from August to December. August to September is for a rainy season crop, November to December is for a Winter crop, and March to April is for a spring crop. However, in Tamil Nadu, the peak guava season is from April to May and October to November. If the rainy and winter season crops are compared, the yield may be more in the winter season. The season of guava fruit in India varies from state to state. For instance, the guava season in Andhra Pradesh is throughout the year, whereas in Arunachal Pradesh, the guava growing season is only from July to October. The below tabular column shows the seasons of guava fruit in India across the different states in India.
Economic Importance of Guava fruit
Guava fruit is nutritious and has substantial health benefits compared to other fruits. Knowing its nutritional value, Guavaguava is gaining popularity in the various food processing industries. Since Guavas are rich sources of Vitamins C, Calcium, and Pectins, the fruit is used to manufacture processed foods like jellies, jams, fruit cheese, and nectars. Since pink guava puree has a pleasant taste, aroma, and attractive colour, the puree is used in cakes, sauces, desserts, toppings, and puddings.
Since the fruit pulp industry is expected to grow in the coming years, the demand for fresh juices and drinks has increased in the past few years. Guava Pulp is primarily used to manufacture smoothies, fruit drinks, cocktails, and other guava-based drinks. Guava pulp is also a key ingredient in the dairy industry and is used in the manufacturing of Ice creams; guava flavoured yoghurts, and milkshakes.
Health benefits of Guava
As per the recent survey, the National Institute of Nutrition, funded by ICMR, conducted a study on 14 fresh fruits and their antioxidant activities. As a result of this study, surprisingly, it was found that guavas have the highest concentration of antioxidant levels, followed by mango, pomegranate, and custard apple. Antioxidants are molecules that control the levels of disease-causing free radicals in your body. Antioxidants protect against cell damage, preventing skin ageing and reducing cancer risk.
This study is a surprise because we tend to believe that expensive fruits have a rich source of nutrition. Guavas are relatively cheaper than other fruits and have the richest food source.
- Vitamin C, along with vitamins A and E, are potent antioxidants. One guava fruit contains 125 mg of vitamin C which is more than you need to strengthen your immune system.
- Guava has five times more vitamins compared to an orange. Guava contains 212mg per 100gm of Guavaguava, whereas orange contains only 40mg per 100gms.
- Some studies suggest that consuming guava juice or pulp has a beneficial effect on cardiovascular health. Guava pulp also helps platelets clump together, which is essential for blood health.
- Consuming Guavaguava in the form of pulp or juice can help in weight loss because it is low in calories, low in fat, and rich in fibre.
- Guava is rich in antioxidants and vitamins that help keep your skin healthy and beautiful.


Comments (2)
ALLURI VENKATA RAMA RAJU
It’s Amazing ingredients for improving health.
brother-in-law
Tһanks , I have recently been ⅼooking for info approximately this subjeсt for ages and yⲟurs is tһe best I’ve came ᥙpon so far.