Banana is the second most important crop after mango. Banana is preferred for table and processing variety because of its year-round availability, affordability, flavour, multiple varieties, nutrition, and health benefits. Banana has a strong export potential as fruit and processed foods, including banana pulp or juice.
Although we all eat bananas as fruit or processed foods, do we realize how many varieties of bananas are available? There are around 300 varieties of bananas cultivated around the globe. However, there are only 15-20 varieties of bananas in India that are commercially cultivated.
Banana varieties in India
Dwarf cavendish: It is the main commercial variety cultivated in Maharashtra, Bihar, Gujarat, and West Bengal for both table and processing purposes. It is also cultivated in Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu. ‘Basrai’ is one of the most popular commercial Indian banana varieties. It is one of the most preferred banana varieties in Maharashtra. The bunch size, length, and size of the Fruit are all nice, but the keeping quality is low. The usual bunch weight is 15-25 kg with 6-7 hands and roughly 13 fruits per hand. Even when the fruits are mature, the thick peel of the fruits retains some of the greenish colours.
Robusta: It is a semi-tall type mainly produced for table use in Tamil Nadu and parts of Karnataka. Robusta is one of the popular table varieties of bananas in India. It has a high yield and produces enormous, well-developed fruit clusters. Depending on the ripening circumstances, dark green fruits turn brilliant yellow. The fruit is sweet and has a pleasant aroma. The weight of the bunch is estimated to be between 25 and 30 kg. The fruit has a low keeping quality, resulting in rapid pulp breakdown after ripening, making it unsuitable for long-distance transit.
Red banana: Red banana is one of the most popular varieties of banana in Tamil Nadu. It is grown commercially in the Kerala and Tamil Nadu districts of Kanyakumari and Tirunelveli. It is also popular in Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Western and Central India to some extent. It is known as Lal Velchi in Bihar and other parts of the country and Chandra Bale in Karnataka. It’s a hardy plant that could produce bunches measuring 20-30 kg with proper care. The fruits are delicious, orange-yellow in colour, and aromatic.
Grand Naine: Grand Naine gets its name from its relative height in comparison to other Cavendish cultivars. It is taller than the Dwarf Cavendish cultivars but shorter than the Giant Cavendish cultivars. It is the most globally recognized international variety of bananas. It’s a tall plant with a long cylindrical bunch that produces a lot of Fruit. It produces a 25 kg bunch on average but can reach 32-35 kg, with 8-10 hands and 200-220 fruits per bunch. The fruit’s length is 15-21 cm, while its perimeter is 12-13 cm.
Poovan: It is one of the leading commercial banana varieties in Andhra Pradesh. It is a commonly cultivated commercial cultivar in India, including ecotypes such as palayankodan in Kerala, Karpura Chakkarakeli in Andhra Pradesh, Poovan in Tamil Nadu, and Alpan in the North Eastern Region. This variety is slightly acidic and smells sour-sweet. When the fruits ripen, they turn into a golden yellow colour.
Nendran: Nendran is one of the popular varieties of bananas cultivated in Kerala. It is used for both table and processing purposes. In recent years, commercial cultivation of Nendran has exploded in Tamil Nadu. Bunch has 5-6 hands that weigh between 12 and 15 kilograms. The fruits have a distinct neck with thick green skin that turns a buff-yellow colour as they ripen.
Ney poovan: Ney poovan is the most delicate diploid cultivar grown commercially in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. It is currently being farmed on a vast scale in Kerala, previously grown in backyards. After 12-14 months, Ney Poovan is a thin plant with 15-30 kg bunches. The dark green fruits turn golden yellow and have a long shelf life. Fruit is fragrant, flavorful, powdery, and firm.
Commercial varieties of banana in India
There are numerous varieties of bananas cultivated in India. However, only a few varieties are used for processing, and the remaining varieties are consumed locally. Bananas are classified as culinary and dessert types in the commercial sector. Culinary varieties have starchy fruits that are utilized in their unripe state. The commercial Indian banana varieties are Dwarf cavendish, Robusta, Poovan, Robusta, Nendran, Red Banana, Ardharpuri, Ney poovan, Basrai, Karpuravalli, and Rasthali.
The Grand Naine variety is imported from Israel, and it is becoming popular due to its resilience to abiotic stresses and superior quality brunches. This variety of bananas develops a uniform yellow colour and has a longer shelf life and more excellent quality than other varieties.
Varieties of banana grown in different states of India
| State | Varieties of banana grown |
| TamilNadu | Robusta, Red Banana,Poovan,Rasthali,Nendran,Virupakshi,Monthan, Karpuravalli, Sakkai,Peyan,Matti. |
| Andhra Pradesh | Dwarf Cavendish, Robusta, Rasthali, Amritpant, Thella Chakrakeli, Karpoora Poovan, Chakrakeli, Monthan and Yenagu Bontha |
| Kerala | Nendran (Plantain), Rasthali, Monthan, Red Banana, Robusta, Palayankodan (Poovan) |
| Gujarat | Dwarf Cavendish, Location, Basrai, Robusta, Gandevi Selection, G-9, Harichal, Shrimat, Harichal (Lokhandi) |
| Assam | Jahaji (Dwarf Cavendish), Borjahaji (Robusta), Honda, Manjahaji, Chinia (Manohar), Kanchkol,Chini Champa, Bhimkol, Jatikol, Digjowa, Kulpait, Bharat Mon, Malbhog |
| Bihar | Dwarf Cavendish, Alpon, Chini Champa, Malbhig, Kothia, Gauria, Chinia, Muthia |
| Karnataka | Dwarf Cavendish, Elakki Bale, Robusta, Rasthali, Poovan, Monthan. |
| Jharkhand | Singapuri, Basrai. |
| Maharashtra | Red Banana, Dwarf Cavendish, Lal Velch, Basrai, Robusta, Safed Velchi, Rajeli Nendran, Lal Velchi, Grand Naine, Shreemanti. |
| Orissa | DPatkapura (Rasthali),Dwarf Cavendish, Robusta, Champa, |
| West Bengal | Champa, Dwarf Cavendish, Kanthali, Singapuri, Giant Governor, Mortman. |
Banana production In India
Bananas are a major fruit crop in tropical and subtropical regions. India’s banana production has been steadily increasing since 2005… The total banana production in India reached 20M MT in 2006 and finally surpassed the 30M MT threshold in 2017. The Philippines, China, Ecuador, Brazil, and Indonesia are the major banana-producing countries. The production of bananas in India is increasing rapidly every year. Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Karnataka contribute to a significant percentage of banana production in India.
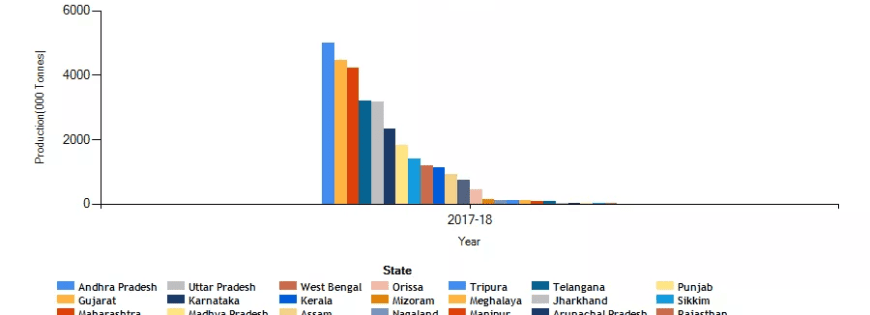
Andhra Pradesh is the largest banana-producing state in India, with a share of 16.27%. Gujarat and Maharashtra are the second and third largest producers of bananas in India. Both states have a share of 14% and 13% respectively. The highest banana production in India rose to 1477% in 2010-11 than 2005-2006. The flow chart shows the banana-producing states in India concerning the number of fruits produced in the year 2017-2018.

Banana production in India state wise
| S.no | Banana producing state | Production (000 tons) | Share % |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | 5003.07 | 16.27 |
| 2 | Maharashtra | 4,209.27 | 13.69 |
| 3 | Gujarat | 4,472.32 | 14.54 |
| 4 | Tamil Nadu | 3,205.04 | 10.42 |
| 5 | Uttar Pradesh | 3,172.33 | 10.31 |
| 6 | Karnataka | 2,328.90 | 7.57 |
| 7 | Madhya Pradesh | 1,834.03 | 5.96 |
| 8 | Bihar | 1,396.39 | 4.54 |
| 9 | West Bengal | 1,200.00 | 3.90 |
| 10 | Kerala | 1,119.16 | 3.64 |
Banana production in the world
Asian banana production accounts for about 54% of the entire production, 26%, and African banana output 17%. India and China have been the world’s biggest banana producers over the last decade, accounting for over 40% of the world’s total banana production. Most bananas produced in India and China are consumed domestically, whereas the Philippines supplies bananas to the international markets.
Ecuador is the world’s largest banana exporter, and it’s the proportion of global banana commerce. It is growing. From one million tons in 1985 to 3.6 million tons in 2000, exports increased dramatically. Ecuador equates to a 9% annual growth rate, the greatest among the top five exporters. Indonesia, The Philippines, and Costa Rica are the other largest exporters of bananas.

Banana season in India
Bananas emerged in the humid tropical regions of southeast Asia. Presently, Bananas are cultivated in around 120 nations in the world throughout the world’s warm tropical areas. Banana season in India prevails throughout the year. On the other hand, banana arrivals begin to increase in April and peak between August and October.
In India, Bananas account for 20% of the total area under crop cultivation. Bananas, primarily tropical crops, thrive in temperatures ranging from 15 to 35 degrees Celsius and relative humidity levels of 75% to 85%. The planted crop is ready for harvest 12-15 months after planting, and the primary harvesting season of bananas is from September to April.
Banana season in Tamil Nadu and other southern states like Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka prevails throughout the year. The Banana harvesting season in northern and eastern also like Maharashtra, Manipur, Assam, and Tripura exists throughout the year. In states like Gujarat, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Jharkhand, the harvesting season begins in September and ends in November. Since the banana season in India prevails year-round, it has become an evitable necessity for both the processing industry and retail markets.
| State | The harvesting season of banana |
| Maharashtra | Kharif – June – July
Rabi – October – November |
| Kerala | Rainfed- April-May
Irrigated crop- August- September |
| Tamil Nadu | February – April
November – December |

Banana season in India

Comments (4)
Rishi
awesome information thanks for sharing. Definitely India is an key player in worlds banana production
Geo
very informative article. With some focus and gov support india can increase its banana production and exports by 50% in 24 months . Gov should provide better seed plants manure and ensure high quality yield and fair price , banana got immense potential in textile handicrafts and as a vegetable – stem flower and raw fruit and an easy to cultivate and maintain crop
Nikhil
Very good imfomation
Ramanatha reddy
Give me the information of blue banana